What is Blockchain Technology? Simple Explanation for Beginners (No Tech Required)
Published on November 05, 2025 by Mrzeeed

Quick Answer
Blockchain is a digital ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that makes the records permanent and tamper-proof. Think of it as a shared notebook that everyone can read, but no one can erase or change past entries. Each "block" contains transaction data, and blocks are "chained" together chronologically, creating an unchangeable record of every transaction.
You've probably heard about blockchain technology in the news, especially when people talk about Bitcoin or cryptocurrency. But what exactly is blockchain? And why is everyone so excited about it? Don't worry – you don't need to be a tech expert to understand it. In this simple guide, we'll explain blockchain technology using everyday examples that anyone can understand.
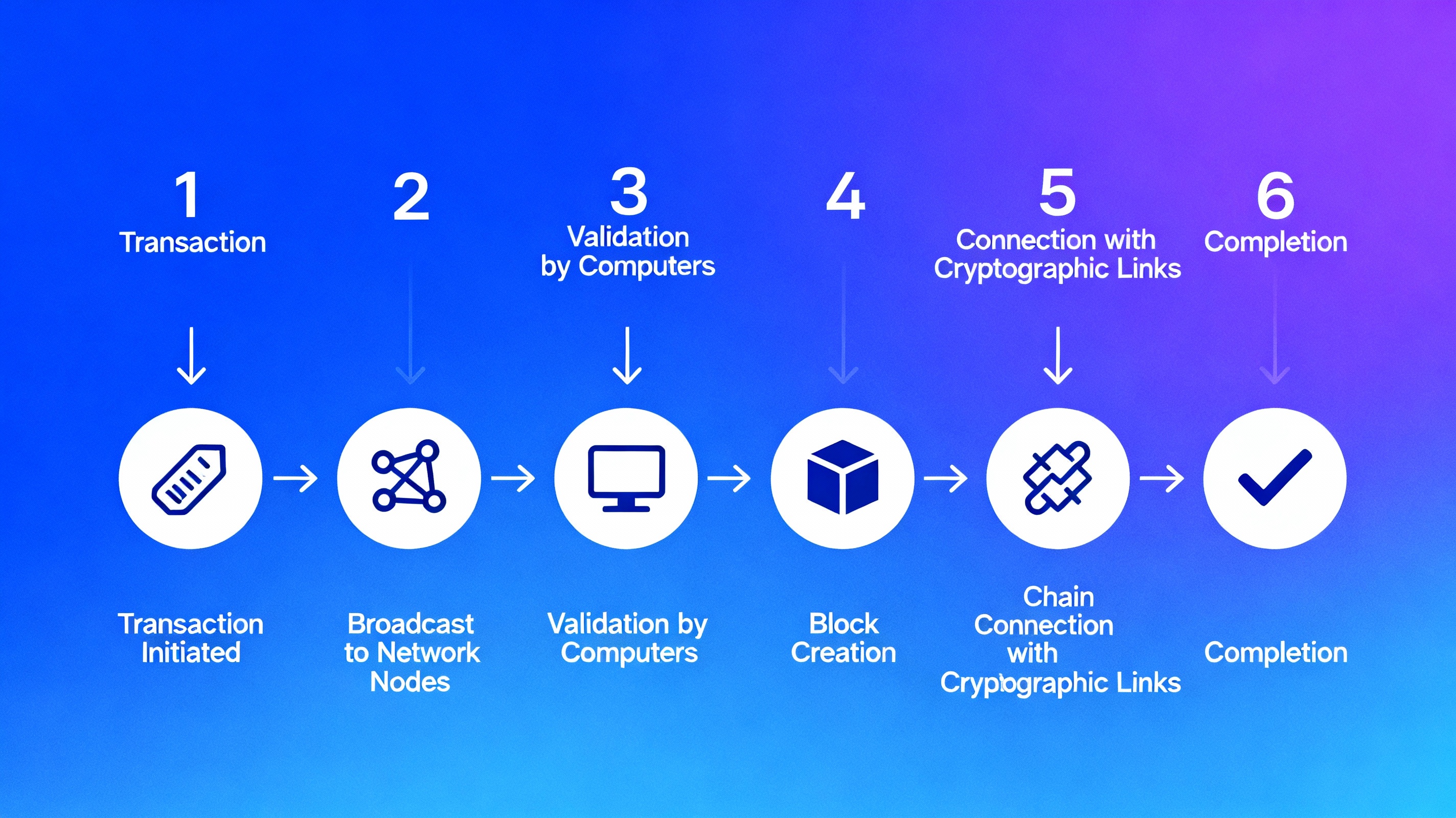
How Blockchain Works: A Visual Step-by-Step Guide
What is Blockchain Technology?
At its core, blockchain is a way to store information that makes it nearly impossible to change, hack, or cheat the system. Instead of storing data in one central location (like a bank's database), blockchain spreads it across a network of computers around the world.
📔 Simple Analogy: The Shared Notebook
Imagine a classroom where every student has an identical notebook. When someone makes a transaction (like borrowing a pencil), everyone writes it down in their notebook at the same time. If someone tries to cheat and change their entry, everyone else's notebooks will show they're lying. That's basically how blockchain works – but with computers instead of notebooks.
How Does Blockchain Work? (Step-by-Step)
Let's break down the blockchain process into simple steps:
A Transaction Happens
Someone initiates a transaction – this could be sending cryptocurrency, recording a contract, or any type of data transfer. For example, Alice wants to send 1 Bitcoin to Bob.
Transaction Broadcast to Network
The transaction is broadcast to all computers (called "nodes") in the blockchain network. These nodes are spread across the world and work together to verify transactions.
Network Validates the Transaction
The network checks if the transaction is legitimate. Does Alice actually have 1 Bitcoin to send? Is this a real transaction? The network uses complex mathematical algorithms to verify this.
Transaction Added to a Block
Once verified, the transaction is combined with other transactions to form a new "block" of data. Think of a block as a page in the shared notebook.
Block Added to the Chain
The new block is added to the existing chain of blocks (hence "blockchain"). Each block is connected to the previous block using cryptographic codes, making it impossible to change past transactions.
Transaction Complete
Bob receives his Bitcoin! The transaction is now permanently recorded on the blockchain and can never be altered or deleted.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Security
Once data is recorded in a blockchain, it's extremely difficult to change. Each block contains a unique code (called a "hash") and the hash of the previous block. If someone tries to tamper with a block, all following blocks would need to be changed too – which is virtually impossible.
Decentralization
Blockchain doesn't rely on one central authority (like a bank). Instead, it's distributed across thousands of computers worldwide. This means no single entity controls the entire network, making it more democratic and resistant to censorship.
Transparency
All transactions on a blockchain are visible to everyone on the network. While users can remain anonymous, every transaction can be traced. It's like having a public ledger that anyone can audit.
Speed & Efficiency
Traditional financial transactions can take days to process, especially international transfers. Blockchain transactions can be completed in minutes or even seconds, and they work 24/7 without bank holidays.
Real-World Blockchain Examples
Blockchain isn't just theory – it's being used right now in many industries:
💰 Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
The most famous use of blockchain. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin use blockchain to record all transactions without needing banks or governments to manage them.
🏥 Healthcare Records
Hospitals are using blockchain to securely store patient records. Doctors can access your medical history instantly, while your data remains private and tamper-proof.
📦 Supply Chain Tracking
Companies like Walmart use blockchain to track food from farm to store. If there's contamination, they can trace it back to the source in seconds instead of days.
🗳️ Voting Systems
Some countries are testing blockchain voting to prevent fraud and ensure every vote is counted accurately. Each vote is recorded permanently and can't be tampered with.
🏠 Real Estate
Property ownership can be recorded on blockchain, making it easier to buy and sell real estate without middlemen, reducing paperwork and fraud.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
| Feature | Traditional Database | Blockchain |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized (one authority) | Decentralized (distributed) |
| Data Modification | Can be edited/deleted | Permanent (immutable) |
| Transparency | Limited (controlled access) | High (public ledger) |
| Trust | Requires trusted intermediary | Trust in math/code |
| Speed | Very fast | Slower (due to verification) |
Common Blockchain Myths (Debunked)
❌ Myth: Blockchain = Bitcoin
Truth: Bitcoin uses blockchain, but blockchain has thousands of other uses beyond cryptocurrency. It's like saying "the internet = email" – email is just one application of internet technology.
❌ Myth: Blockchain is Anonymous
Truth: Blockchain is pseudonymous, not anonymous. While your real name isn't attached to transactions, every transaction is publicly visible and can potentially be traced back to you.
❌ Myth: Blockchain is Unhackable
Truth: While blockchain is extremely secure, it's not 100% unhackable. Small blockchains with few nodes are more vulnerable. However, major blockchains like Bitcoin are incredibly difficult to attack due to their size and distribution.
❌ Myth: Blockchain Will Replace All Databases
Truth: Blockchain is not suitable for every use case. Traditional databases are faster and more efficient for many applications. Blockchain shines when you need transparency, decentralization, and immutability.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
-
✅
Enhanced Security: Cryptographic encryption makes data extremely secure
-
✅
Reduced Costs: Eliminates intermediaries, reducing transaction fees
-
✅
Faster Transactions: No need to wait for bank processing times
-
✅
Transparency: All participants can view transaction history
-
✅
Traceability: Easy to track items through supply chains
-
✅
Automation: Smart contracts can execute automatically
Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
-
❌
Energy Consumption: Some blockchains (like Bitcoin) use massive amounts of electricity
-
❌
Scalability Issues: Can't process as many transactions as traditional systems
-
❌
Storage Requirements: The blockchain grows forever and takes up disk space
-
❌
Complexity: Difficult for average users to understand and use
-
❌
Irreversible Transactions: Mistakes can't be undone
-
❌
Regulatory Uncertainty: Laws around blockchain are still evolving
Types of Blockchain Networks
Not all blockchains are the same. There are different types depending on who can access them:
1. Public Blockchain
Anyone can join and participate. Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum. Completely transparent and decentralized.
Best for: Cryptocurrencies, public records
2. Private Blockchain
Access is restricted to specific participants. Used by businesses for internal operations.
Best for: Corporate applications, internal auditing
3. Consortium Blockchain
Controlled by a group of organizations rather than one entity. Semi-decentralized.
Best for: Banking consortiums, supply chain groups
4. Hybrid Blockchain
Combines public and private elements. Some data is public, some is restricted.
Best for: Government services, healthcare
The Future of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is still in its early stages, but experts predict massive growth in the coming years:
🚀 Mass Adoption by 2030
Analysts predict that blockchain could be as common as the internet by 2030, with billions of people using blockchain-based applications daily.
🏦 Banking Revolution
Major banks are already investing in blockchain technology. In the future, most financial transactions could happen on blockchain networks.
🌍 Government Services
Governments worldwide are exploring blockchain for identity management, property records, and voting systems.
⚡ Improved Technology
New blockchain technologies are solving current problems like slow speeds and high energy consumption. Future blockchains will be faster, cheaper, and more eco-friendly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is blockchain the same as cryptocurrency? ▼
No. Blockchain is the technology, and cryptocurrency is just one application of it. Blockchain can be used for many things beyond digital money.
Can blockchain be hacked? ▼
While blockchain is extremely secure, it's not 100% impossible to hack. However, major blockchains with thousands of nodes are incredibly difficult and expensive to attack, making hacking impractical.
Do I need to understand coding to use blockchain? ▼
No! Just like you don't need to understand how the internet works to browse websites, you don't need coding knowledge to use blockchain applications. Many user-friendly apps are available.
How much does it cost to use blockchain? ▼
It varies. Some blockchains have transaction fees (like Bitcoin's network fees), while others are nearly free. Many applications built on blockchain are free to use.
Is blockchain legal? ▼
Yes, blockchain technology itself is legal in most countries. However, regulations around specific uses (like cryptocurrency) vary by country. Always check your local laws.
How do I start using blockchain? ▼
The easiest way is to start with a cryptocurrency wallet app or explore blockchain-based applications. Many platforms like Faucet.Studio let you earn and use blockchain-based tokens without technical knowledge.
Conclusion: Why Blockchain Matters
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing how we store data, conduct transactions, and trust each other online. While it may seem complex at first, the core concept is simple: a secure, transparent, and decentralized way to record information that can't be tampered with.
Key Takeaways:
- • Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that creates permanent, tamper-proof records
- • It's not just for cryptocurrency – blockchain has applications in healthcare, supply chain, voting, and more
- • The technology offers enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency compared to traditional systems
- • While blockchain has challenges (energy use, scalability), new solutions are constantly being developed
- • You don't need to be a tech expert to benefit from blockchain technology
Whether blockchain becomes as transformative as the internet remains to be seen, but one thing is certain: this technology is here to stay, and understanding it now puts you ahead of the curve.
Ready to Experience Blockchain?
Start earning cryptocurrency and experience blockchain technology firsthand with no investment required!
Try Faucet.Studio - Free PEPE Tokens →

